Easy! IT | Security | Sender Policy Framework
This article is a rough explanation of the Sender Policy Framework.
Everything might be not exactly correct in this article but it’s very useful for beginners to understand IT terms. If you want to learn IT but you don’t have any experience to work in the IT industry, I wish it helps you to understand IT. And I hope that this article motivates you to study IT more.
Let’s start our 3 minutes lesson!
What is the Sender Policy Framework?
- SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework.
- SPF is an email authentication method to check who sends the email.
- SPF helps to prevent your mail users from receiving spam mails.
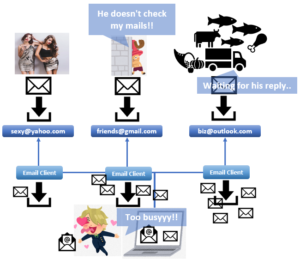
1. Email service
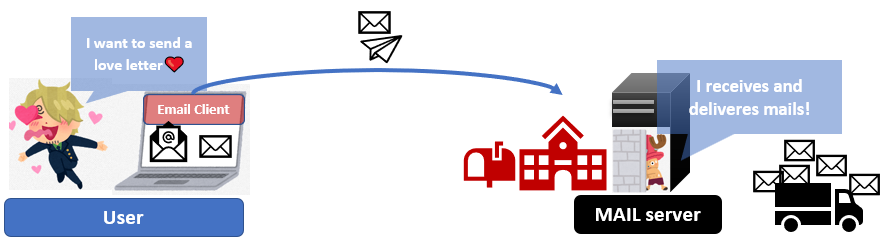
You can send messages with a digital letter called an email. Users can send an email with a client (mail application such as Gmail, yahoo mail, outlook and so on), and mail servers receive and deliver them.
In short, an email is a letter in a computing world, and the mail server is a post office in that world.
2. Why You Need SFP
SMTP is a very nice guy.
What is SMTP?: Easy! IT | Protocol | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | Japan Teams
SMTP is well-known as a super nice guy, which all emails are welcome to and sends them. But hackers always look for kindness(weakness). They send emails pretending to be someone. Then people need some measures to prevent hackers from sending mails as the different people. SPF is developed as the solution, which is the way to link an email to a domain.
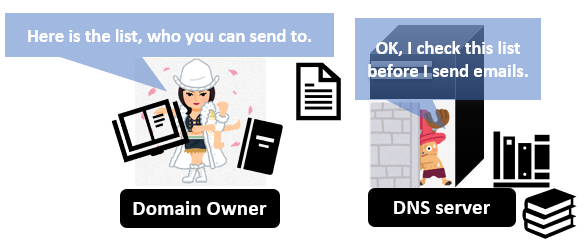
What SPF action is:
- The domain owner publishes the list of allowed senders.
- Email receivers check the list to if a sender is allowed.
- If so, the link between the domain and the email is established.
What is DNS?: IT Learning | Network | DNS | Japan Teams
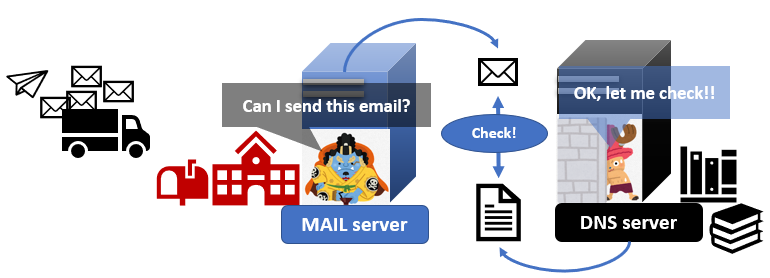
More details:Publishing a policy
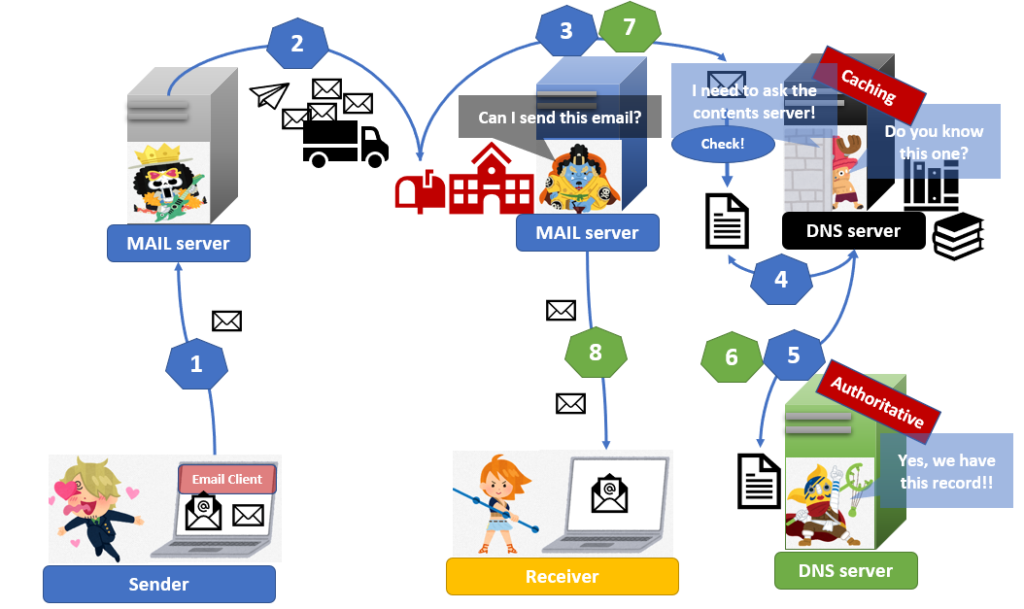
1. Publishing a policy
A domain administrator adds additional records to their exiting DNS to identify the machines authorized to send an email. That record is called an SPF record. The record contains IP addresses that are verified to send emails on behalf of their domains.
2. Lookup SPF record
When a mail server receives an email via SMTP, a mail server asks an SPF record to the DNS server which MAIL FROM command specifies.
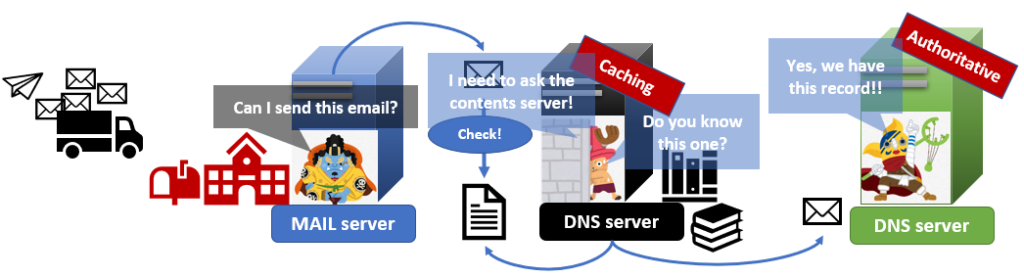
3.Caching DNS checks the SPF record
Caching DNS server asks for a content DNS(Authoritative DNS) server if it doesn’t cache the SPF record.
4. Comparing IP addresses
After receiving the SPF record from an authoritative server, a caching DNS server answers the SPF record to a mail server that receives the email. Then, a mail server compares the IP address from the SPF record with the IP address of the mail server that sent the email. If IP addresses match, an SPF verify succeeds. If those IP addresses are different, an SPF verify fails and the mail server rejects the mail.
What is an SPF record?
SPF record is a type of DNS record. Actually, A TXT record is used as an SPF record.
What is the TXT record?: Easy! IT | Server | TXT Record | Japan Teams
The format is:
“v=spf1 +ip4:192.168.1.1/24 +ip4:10.254.1.2/24 -all”
“v=”: It defines the version of SPF used.
“+”: This character means “accept”. So IP addresses after this one can be accepted as a sender mail server.
“ip4:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xx”: Those IP addresses are allowed to send emails.
“-“: This means “fail”. So The value after “-” is usually “all” for security.
Summary of SPF

Information source: What is SPF: Sender Policy Framework and Why it is Important for Email (dmarcian.com), Sender Policy Framework – Wikipedia
fin
|
|
![[商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。] [商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。]](https://hbb.afl.rakuten.co.jp/hgb/20e00fbc.dcc74e5c.20e00fbd.9b562f6c/?me_id=1278256&item_id=16173564&pc=https%3A%2F%2Fthumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp%2F%400_mall%2Frakutenkobo-ebooks%2Fcabinet%2F6735%2F2000004946735.jpg%3F_ex%3D240x240&s=240x240&t=picttext)